Saturday, March 28, 2015
Day 9: Maximum Power Transfer and Non-Ideal Power Source
 |
| This is showing that the resistance that creates the maximum power is when the resistance in the thevenin circuit is equal to that of the thevenin resistance. |
 |
| This is calculating max power in a circuit. |
 |
| This is the circuit using the wavefunction to generate a voltage and measure the current. and to measure the resistance inside of the analog discovery. |
Day 8: Thevenin's Theorem
 |
| This circuit is simplified to measure the one resistance and the one voltage so that as you change one resistance it is easier to calculate its effects on the system. |
 |
| This is everycircuit, it should the current and voltage throughout a theoretical circuit. |
 |
| This is the circuit that is used for the experiment using a potentiometer to change the resistance. |
 |
| This is the thevenin circuit. |
Day 7: Time Varying Signals
 |
| This is the set up for a BJT curve tracer. It contains two voltages that vary differently as they have different effects on each other as they travel through the BJT. |
 |
| This is the effects of a change in the resistance on the circuit. The wavelength is constant but the amplitude is decreased. |
 |
| This is a closer look at the BJT Curve Tracer set up. It has one voltage source that is DC and the other is a step voltage source. |
 |
| This is the set up of the circuit. The graph is what is expected to see from the voltage out of the transistor. |
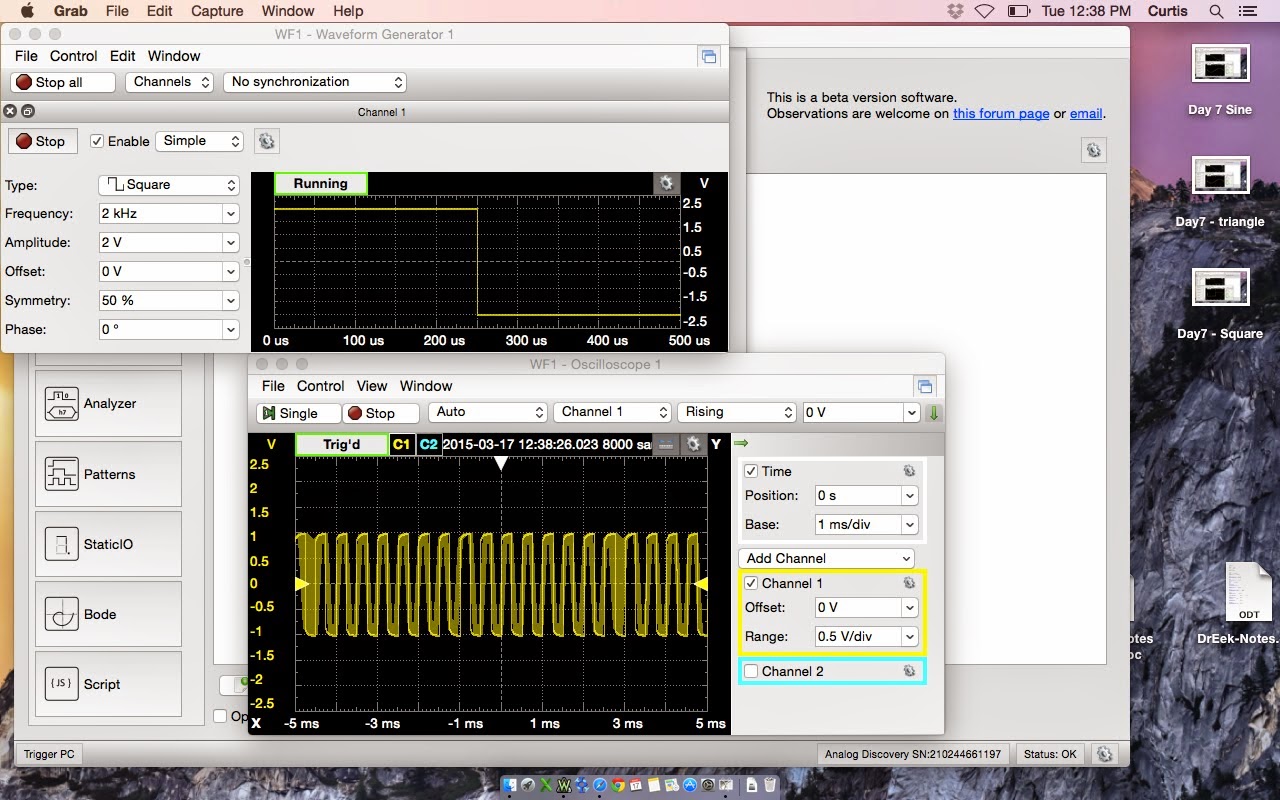 |
| This the view of the voltage coming from the waveform and the oscilloscope measuring the output. |
 |
| Using a triangle voltage supplied from the wave form, the oscilloscope measures a triangular wave output. |
 |
| This waveform uses a sinusoidal wave. The oscilloscope measures a sinusoidal wave. |
 |
| This is the graph as the voltage is stepped up and it reaches its limit across the transistor. |
Day 6: Nodal Analysis III
 |
| Even though this lab is called Nodal Analysis. I am doing Mesh Analysis. Cause I am my own boss. |
 |
| This circuit contains three full loops that cover each of the circuit components in the smallest loops possible. |
 |
| The voltage drop is measure across a resistor. |
 |
| Every piece of the circuit is analyzed. This has a theoretical voltage across the resistor and then the measure voltage across the resistor in order to create a percentage uncertainty. |
Day 5: Nodal Analysis
 |
| This is an example of nodal analysis. Using I=V/R and looking at currents coming and leaving at a node to calculate voltages as the current is conserved. |
 |
| This is a circuit using three resistors and measuring voltage. |
 |
| This circuit allows for the measurement of the voltage at the node 2 using nodal analysis and then measuring the value and using % error as theoretical versus experimental. |
Day 4: Temperature Measurement System
 |
| This is just a sample circuit calculating the voltage across a resistor from given two current sources. This would be a lot easier if I had known source conversions... |
 |
| This video shows the heat actually decreasing the resistance and increasing the voltage drop across the resistor. |
Tuesday, March 10, 2015
Day 3 : Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs)
 |
| The first rule of hot dog cooking club is to not get cheap hot dogs that smell like hair when they are cooked. |
 |
| In order to get a thoroughly cooked dog, Make sure you us a large voltage source. |
 |
| This is a voltage source and a capacitor. A graph of the voltage from the capacitor when it is supplied with a square wave. |
 |
| This is a circuit conversion to create a more simple circuit that can be easily analyzed for the adjustments in one resistor. |
 |
| There is a photo-resistor in this circuit which decreases the resistance in the system so that the LED receives a higher current when it gets dark. |
 |
| This is the circuit using the photo-resistor. |
Monday, March 9, 2015
matrix laboratory
 |
| This is just simple input steps on free mat. |
 |
| This is designating variables. |
 |
| Creating Matrices. |
 |
| Multiplying Matrices. |
 |
| Outputting individual rows and columns. |
 |
| Printing out sinusoidal functions. |
 |
| This is an attempt at getting the program to create a file and access it. It gave me an error and then questioned my authority as admin. |
 |
| No one questions my authority. This program cross the line and so I handled it. It still wont access the functions I save. Freemat 1: MikE 0 |
Tuesday, March 3, 2015
Day 2: We did a lot of stuff on this day.
 |
| This is a simple circuit experiment understanding if connecting this circuit will change the brightness of the light. |
 |
| The lights stayed the same and the middle light did not light up. That is not the middle light you see there. |
 |
| These are graphs that relationships between voltage and current that can and cannot exist. The ones on the right are labeled A, which could be a diode, and B, which is impossible. |
 |
| This is the Analog Discovery. It has been compared to Thor's Hammer, to the scientist that made the Steve Austin, and if it were a heat engine it would be have a 31% rating for efficiency. |
 |
| This is just the measurement of the resistor before an experiment was done to measure the change in current as the voltage is adjusted. |
 |
| This is all the data collected using the RC. |
 |
| This is the circuit that the experiment used. |
 |
| This is the graph of change of current over voltage. They have a linear relationship in this circuit, because it only consists of a resistor and a voltage source. |
 |
| This is an equation to calculate the number of components from the number of independent circuits and nodes. |
 |
| This is the use of KVL to calculate the current and the voltage across a point. |
 |
| This is a diagram of the circuit that was created for the experiment. It also contains the values of the voltage supplied by the analog discovery and the measure current. |
 |
| This is showing the change in the bulb if another voltage source is brought in parallel to one of the bulbs. |
 |
| These are both wrong because the voltage source in parallel so neither of the bulbs change. |
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)










